Publications
Books, Journal and conference papers
You can find the most up-to-date list of my publications on Google Scholar
2025
-
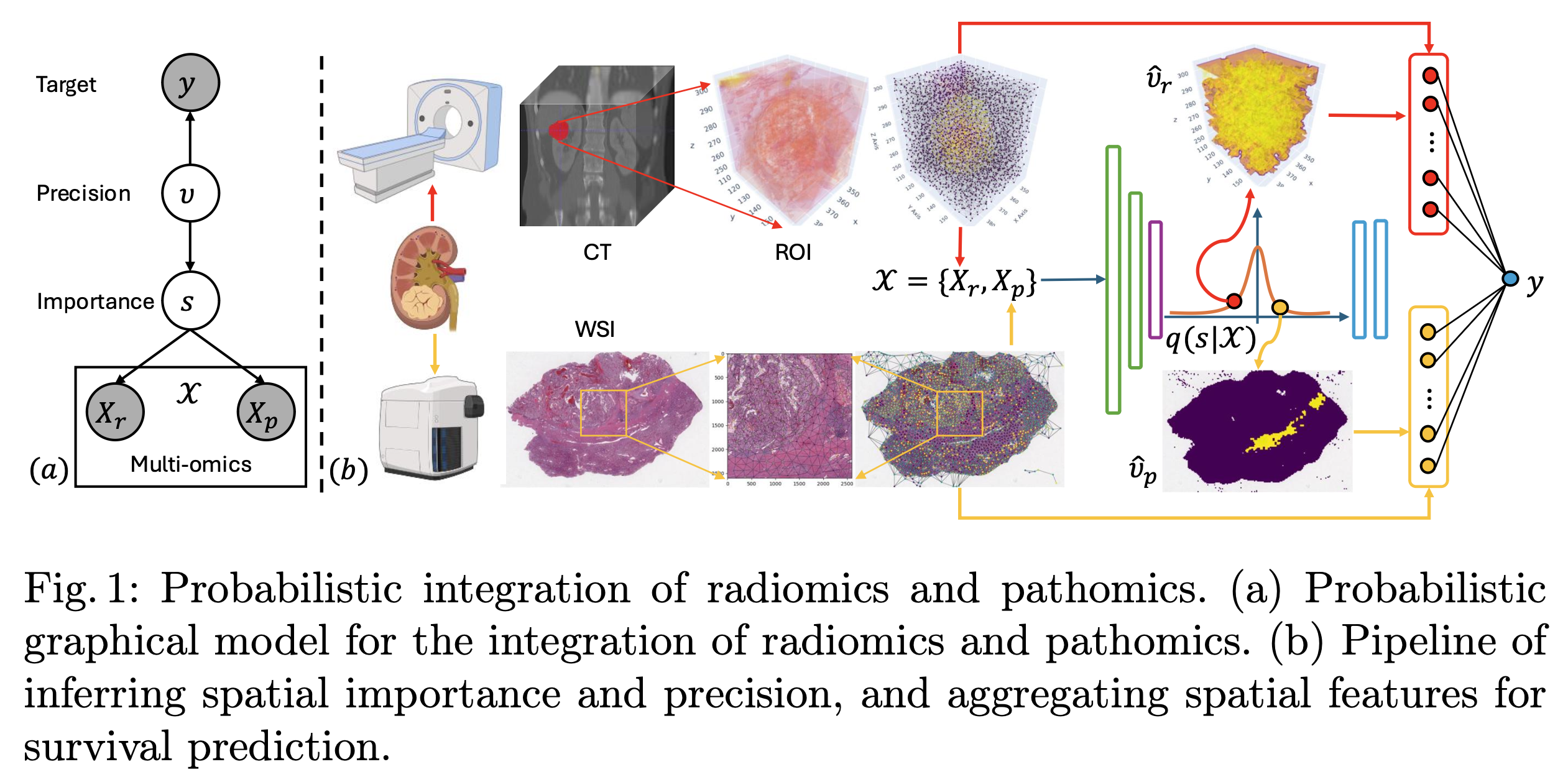 Probabilistic Integration of Renal Cancer Radiology and Pathology Using Graph Neural NetworksIn Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2025, 2025
Probabilistic Integration of Renal Cancer Radiology and Pathology Using Graph Neural NetworksIn Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2025, 2025Kidney tumors can be highly heterogeneous from the microscopic to the macroscopic scale. To address this, we propose a sparsity-informed probabilistic integration of radiomics and pathomics for kidney cancer analysis. We construct radiology and pathology graphs to model spatial correlations, then use a probabilistic method and graph neural networks to identify biomarkers and aggregate spatial features. Our validation shows that this integrated approach significantly outperforms traditional methods in kidney survival analysis, achieving a notable improvement of 0.084 in the concordance index, enabling better prognostic assessments for kidney cancer patients. The source code has been released by https://github.com/shangqigao/RadioPath.
@inproceedings{Gao2025miccai, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Gao, Shangde and Machado, Ines and Crispin-Ortuzar, Mireia}, editor = {Gee, James C. and Alexander, Daniel C. and Hong, Jaesung and Iglesias, Juan Eugenio and Sudre, Carole H. and Venkataraman, Archana and Golland, Polina and Kim, Jong Hyo and Park, Jinah}, title = {Probabilistic Integration of Renal Cancer Radiology and Pathology Using Graph Neural Networks}, booktitle = {Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention -- MICCAI 2025}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Springer Nature Switzerland}, address = {Cham}, pages = {564--573}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-032-05162-2_54}, dimensions = {true} } -
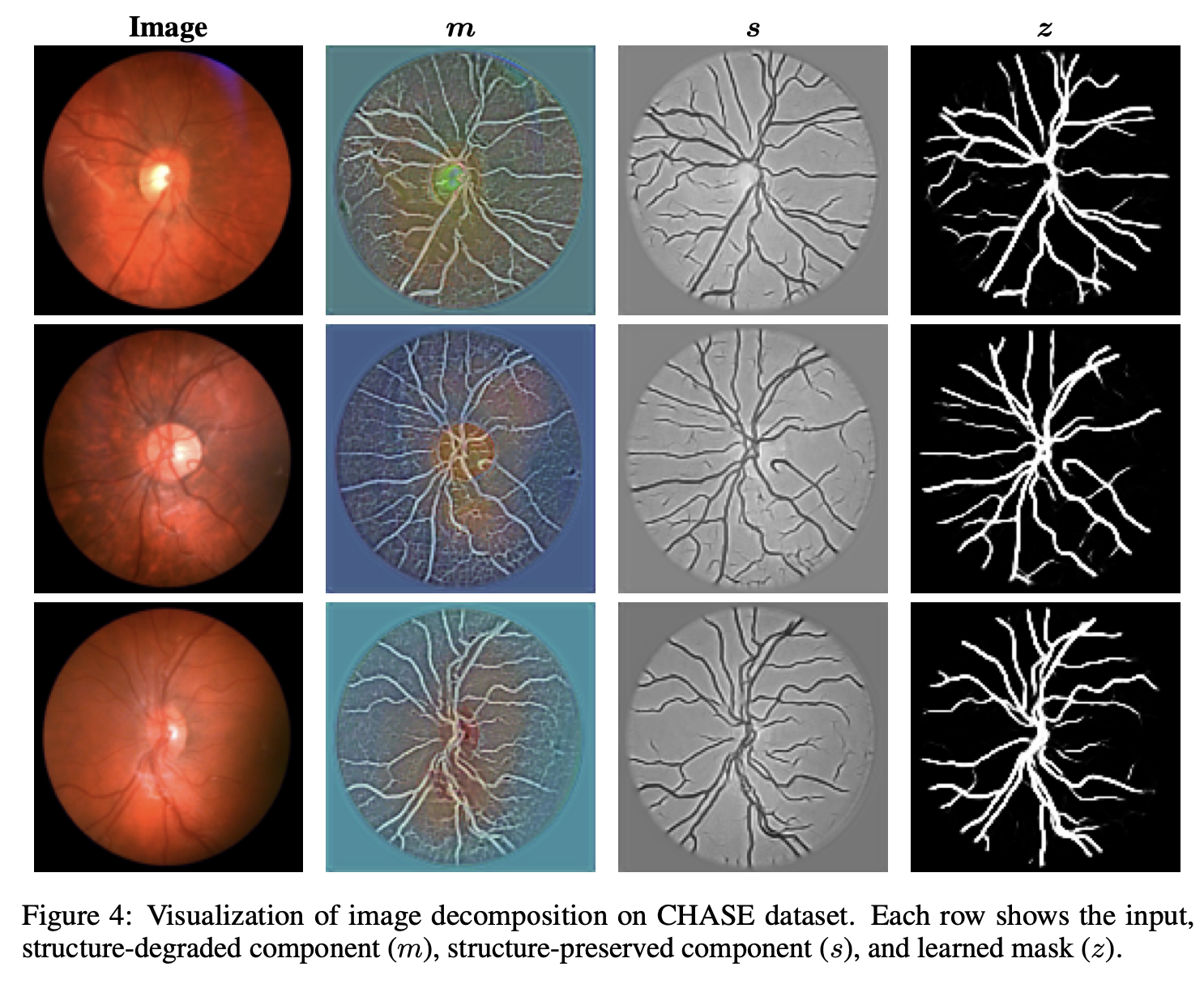 Towards Generalizable Retina Vessel Segmentation with Deformable Graph PriorsIn The Thirty-ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Nov 2025
Towards Generalizable Retina Vessel Segmentation with Deformable Graph PriorsIn The Thirty-ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Nov 2025Retinal vessel segmentation is critical for medical diagnosis, yet existing models often struggle to generalize across domains due to appearance variability, limited annotations, and complex vascular morphology. We propose GraphSeg, a variational Bayesian framework that integrates anatomical graph priors with structure-aware image decomposition to enhance cross-domain segmentation. GraphSeg factorizes retinal images into structure-preserved and structure-degraded components, enabling domain-invariant representation. A deformable graph prior, derived from a statistical retinal atlas, is incorporated via a differentiable alignment and guided by an unsupervised energy function. Experiments on three public benchmarks (CHASE, DRIVE, HRF) show that GraphSeg consistently outperforms existing methods under domain shifts. These results highlight the importance of jointly modeling anatomical topology and image structure for robust generalizable vessel segmentation.
@inproceedings{liu2025towards, author = {Liu, Ke and Gao, Shangde and Fu, Yichao and Gao, Shangqi}, title = {Towards Generalizable Retina Vessel Segmentation with Deformable Graph Priors}, booktitle = {The Thirty-ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems}, month = nov, year = {2025}, url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=zVkbsGlKn9}, dimensions = {true} }
2024
-
 Characterising borderline areas in bladder tumour grading with Bayesian graph neural networksShangqi Gao, Lisa Browning, Nasullah Khalid Alham, and 5 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nov 2024
Characterising borderline areas in bladder tumour grading with Bayesian graph neural networksShangqi Gao, Lisa Browning, Nasullah Khalid Alham, and 5 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nov 2024Urothelial carcinoma is the most common bladder cancer whose grading is critical to clinical decision-making. The WHO 2004 grading system classifies urothelial carcinoma into either low grade or high grade, but sometimes cases sit on the border between grades. This makes assessment by the pathologist challenging but could potentially lead to under-treatment or overtreatment. The aim of this study was to use deep learning methods to identify and characterise borderline areas in whole slide images (WSIs) from bladder tumour cases. We constructed graphs on WSIs to accelerate computation, where positive unlabeled learning was utilized, accommodating the partial annotation strategy deployed in clinics. We used Bayesian deep learning for carcinoma classification, where we modeled the borderline as prediction uncertainty quantified by Bayesian graph neural networks. Our experiments showed promising performance of our approach in carcinoma detection and classification, with a potential use case to highlight and better characterise areas on the border for high grade and low grade to pathologists.
-
 Comprehensive Analysis and Computing of Real-World Medical Images: First MICCAI Challenge, CARE 2024, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2024, Marrakesh, Morocco, October 10, 2024, Proceedings, Marrakesh, Morocco, Nov 2024
Comprehensive Analysis and Computing of Real-World Medical Images: First MICCAI Challenge, CARE 2024, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2024, Marrakesh, Morocco, October 10, 2024, Proceedings, Marrakesh, Morocco, Nov 2024@proceedings{CARE2024, title = {Comprehensive Analysis and Computing of Real-World Medical Images: First MICCAI Challenge, CARE 2024, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2024, Marrakesh, Morocco, October 10, 2024, Proceedings}, editor = {Zhuang, Xiahai and Ding, Wangbin and Wu, Fuping and Gao, Shangqi and Li, Lei and Wang, Sihan}, year = {2024}, isbn = {978-3-031-87008-8}, publisher = {Springer-Verlag}, address = {Berlin, Heidelberg}, location = {Marrakesh, Morocco}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-87009-5}, }
2023
-
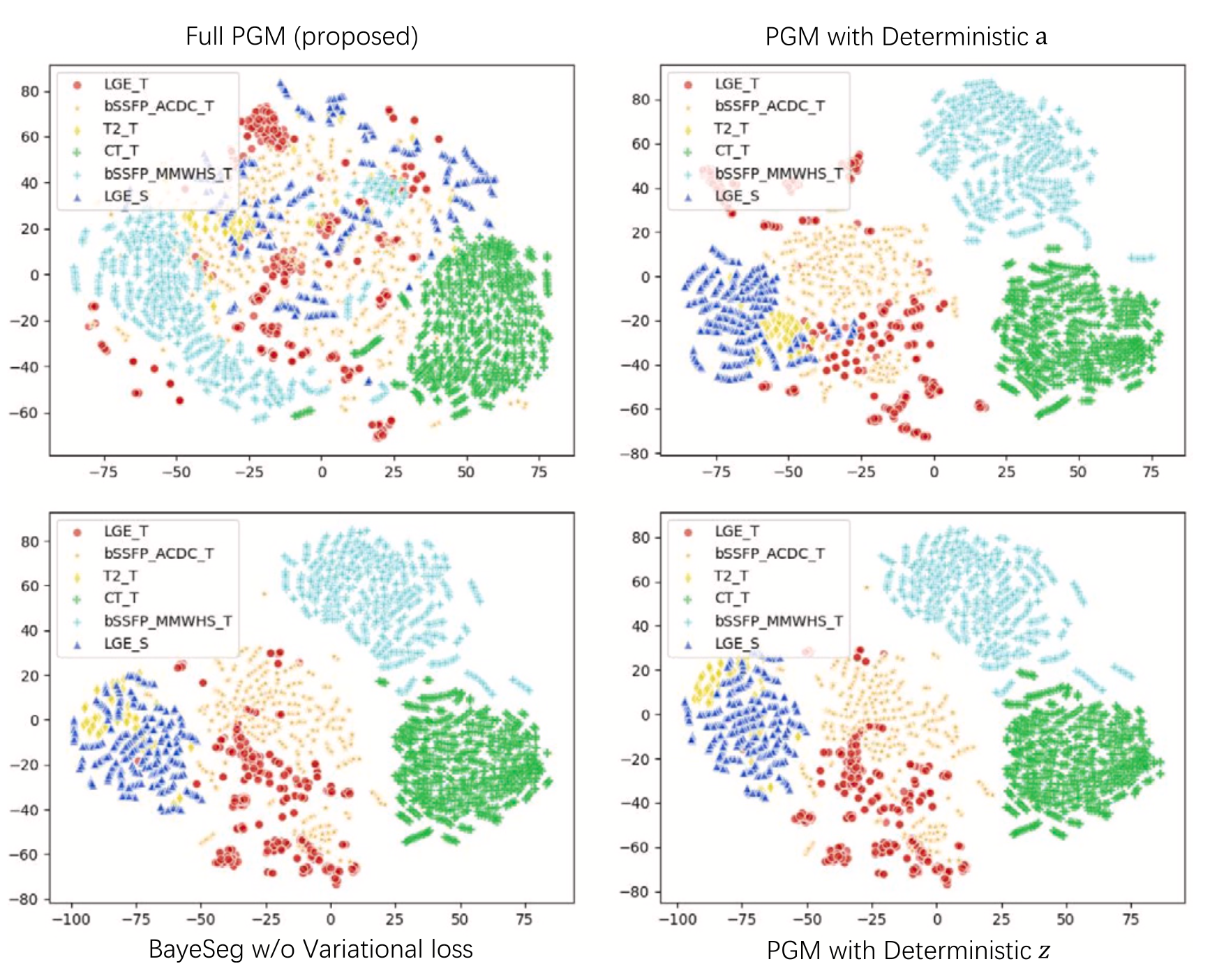 BayeSeg: Bayesian modeling for medical image segmentation with interpretable generalizabilityShangqi Gao, Hangqi Zhou, Yibo Gao, and 1 more authorMedical Image Analysis, Nov 2023
BayeSeg: Bayesian modeling for medical image segmentation with interpretable generalizabilityShangqi Gao, Hangqi Zhou, Yibo Gao, and 1 more authorMedical Image Analysis, Nov 2023Elsevier-MedIA 1st Prize & Medical Image Analysis MICCAI Best Paper Award 2023
Due to the cross-domain distribution shift aroused from diverse medical imaging systems, many deep learning segmentation methods fail to perform well on unseen data, which limits their real-world applicability. Recent works have shown the benefits of extracting domain-invariant representations on domain generalization. However, the interpretability of domain-invariant features remains a great challenge. To address this problem, we propose an interpretable Bayesian framework (BayeSeg) through Bayesian modeling of image and label statistics to enhance model generalizability for medical image segmentation. Specifically, we first decompose an image into a spatial-correlated variable and a spatial-variant variable, assigning hierarchical Bayesian priors to explicitly force them to model the domain-stable shape and domain-specific appearance information respectively. Then, we model the segmentation as a locally smooth variable only related to the shape. Finally, we develop a variational Bayesian framework to infer the posterior distributions of these explainable variables. The framework is implemented with neural networks, and thus is referred to as deep Bayesian segmentation. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results on prostate segmentation and cardiac segmentation tasks have shown the effectiveness of our proposed method. Moreover, we investigated the interpretability of BayeSeg by explaining the posteriors and analyzed certain factors that affect the generalization ability through further ablation studies. Our code is released via https://zmiclab.github.io/projects.html.
@article{GAO2023102889, title = {BayeSeg: Bayesian modeling for medical image segmentation with interpretable generalizability}, journal = {Medical Image Analysis}, volume = {89}, pages = {102889}, year = {2023}, issn = {1361-8415}, doi = {10.1016/j.media.2023.102889}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1361841523001494}, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Zhou, Hangqi and Gao, Yibo and Zhuang, Xiahai}, keywords = {Image segmentation, Interpretation and generalization, Statistical modeling, Variational Bayes}, dimensions = {true}, } -
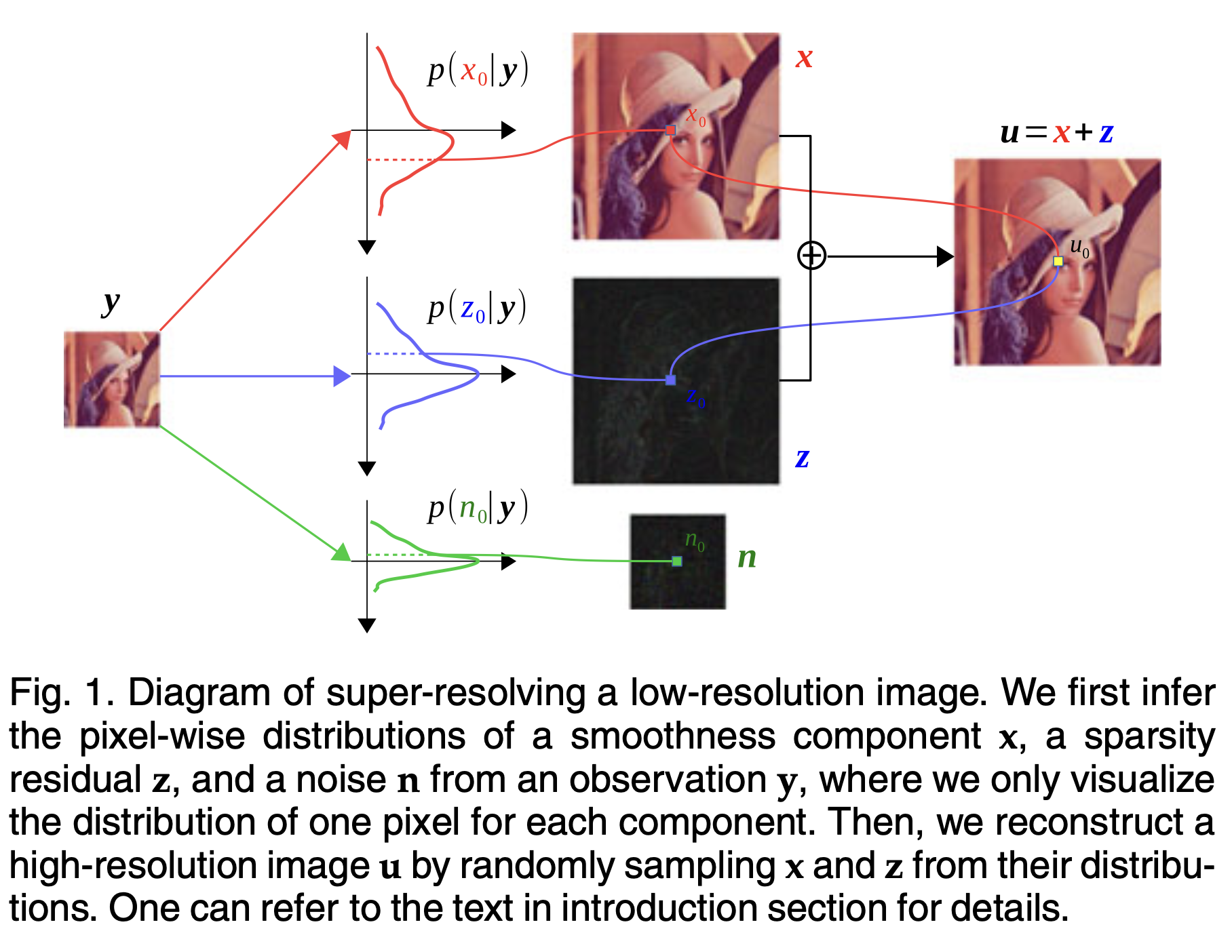 Bayesian Image Super-Resolution With Deep Modeling of Image StatisticsShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Nov 2023
Bayesian Image Super-Resolution With Deep Modeling of Image StatisticsShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Nov 2023Modeling statistics of image priors is useful for image super-resolution, but little attention has been paid from the massive works of deep learning-based methods. In this work, we propose a Bayesian image restoration framework, where natural image statistics are modeled with the combination of smooth- ness and sparsity priors. Concretely, firstly we consider an ideal image as the sum of a smoothness component and a sparsity residual, and model real image degradation including blurring, downscaling, and noise corruption. Then, we develop a variational Bayesian approach to infer their posteriors. Finally, we implement the variational approach for single image super-resolution (SISR) using deep neural networks, and propose an unsupervised training strategy. The experiments on three image restoration tasks, i.e., ideal SISR, realistic SISR, and real-world SISR, demonstrate that our method has superior model generalizability against varying noise levels and degradation kernels and is effective in unsupervised SISR. The code and resulting models are released via https://zmiclab.github.io/projects.html.
@article{Gao9744488, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Zhuang, Xiahai}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence}, title = {Bayesian Image Super-Resolution With Deep Modeling of Image Statistics}, year = {2023}, volume = {45}, number = {2}, pages = {1405-1423}, keywords = {Image restoration;Bayes methods;Computational modeling;Mathematical models;Superresolution;Task analysis;Image denoising;Image super-resolution;variational inference;neural network;generative learning}, doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3163307}, dimensions = {true}, } -
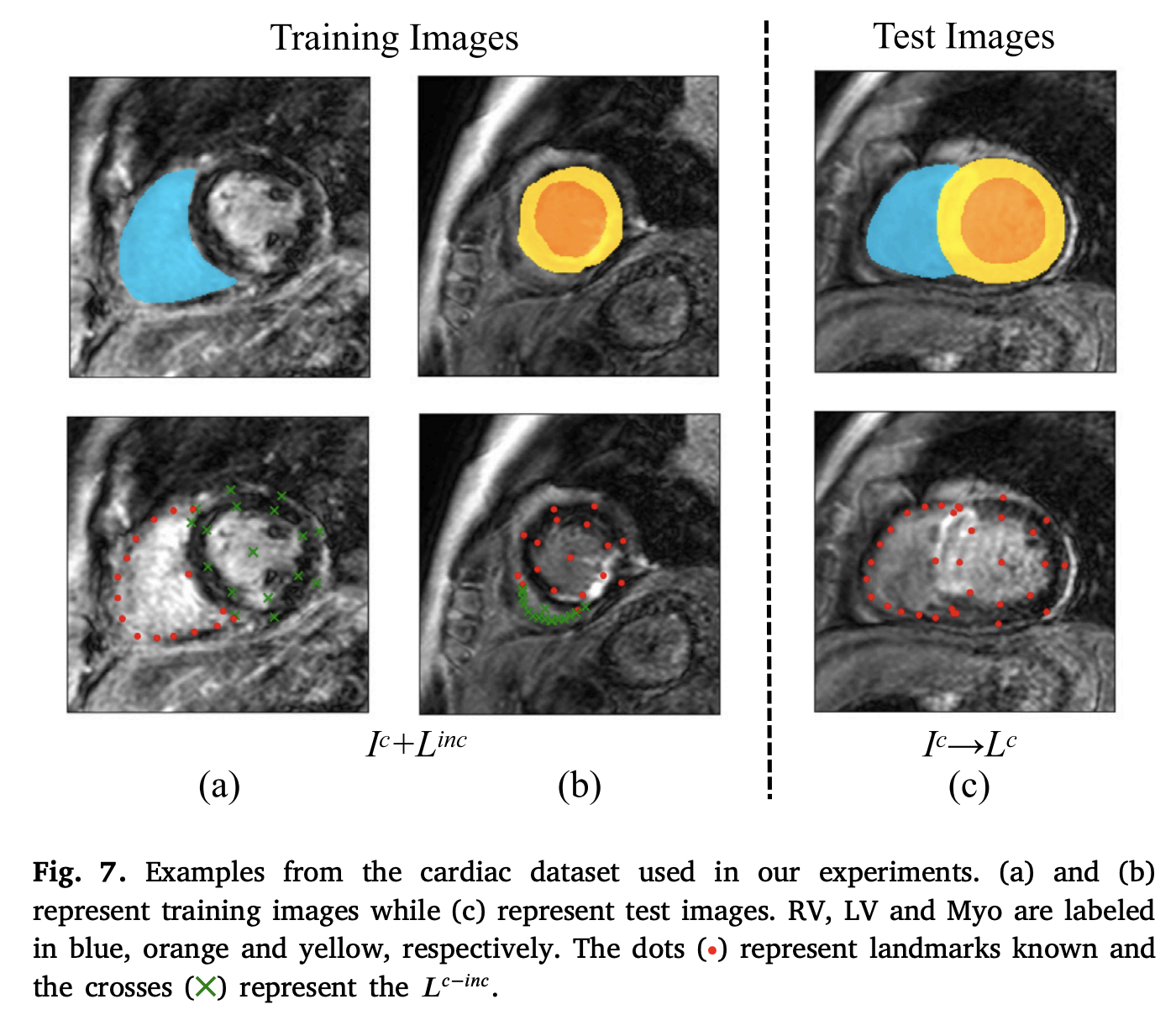 Multi-target landmark detection with incomplete images via reinforcement learning and shape prior embeddingKaiwen Wan, Lei Li, Dengqiang Jia, and 9 more authorsMedical Image Analysis, Nov 2023
Multi-target landmark detection with incomplete images via reinforcement learning and shape prior embeddingKaiwen Wan, Lei Li, Dengqiang Jia, and 9 more authorsMedical Image Analysis, Nov 2023Medical images are generally acquired with limited field-of-view (FOV), which could lead to incomplete regions of interest (ROI), and thus impose a great challenge on medical image analysis. This is particularly evident for the learning-based multi-target landmark detection, where algorithms could be misleading to learn primarily the variation of background due to the varying FOV, failing the detection of targets. Based on learning a navigation policy, instead of predicting targets directly, reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods have the potential to tackle this challenge in an efficient manner. Inspired by this, in this work we propose a multi-agent RL framework for simultaneous multi-target landmark detection. This framework is aimed to learn from incomplete or (and) complete images to form an implicit knowledge of global structure, which is consolidated during the training stage for the detection of targets from either complete or incomplete test images. To further explicitly exploit the global structural information from incomplete images, we propose to embed a shape model into the RL process. With this prior knowledge, the proposed RL model can not only localize dozens of targets simultaneously, but also work effectively and robustly in the presence of incomplete images. We validated the applicability and efficacy of the proposed method on various multi-target detection tasks with incomplete images from practical clinics, using body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), cardiac MRI and head CT datasets. Results showed that our method could predict whole set of landmarks with incomplete training images up to 80% missing proportion (average distance error 2.29 cm on body DXA), and could detect unseen landmarks in regions with missing image information outside FOV of target images (average distance error 6.84 mm on 3D half-head CT). Our code will be released via https://zmiclab.github.io/projects.html.
2022
-
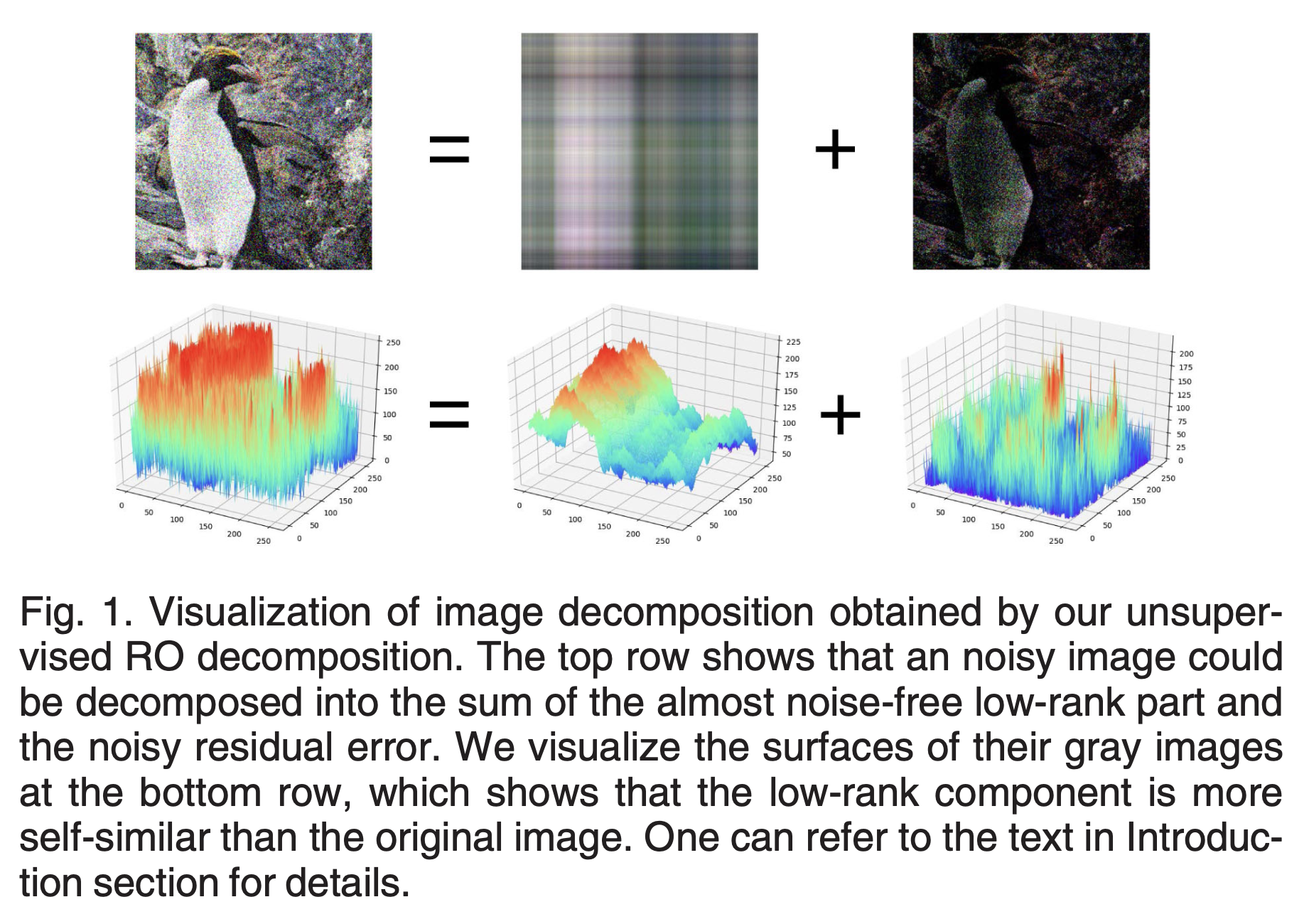 Rank-One Network: An Effective Framework for Image RestorationShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Nov 2022
Rank-One Network: An Effective Framework for Image RestorationShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Nov 2022The principal rank-one (RO) components of an image represent the self- similarity of the image, which is an important property for image restoration. However, the RO components of a corrupted image could be decimated by the procedure of image denoising. We suggest that the RO property should be utilized and the decimation should be avoided in image restoration. To achieve this, we propose a new framework comprised of two modules, i.e., the RO decomposition and RO reconstruction. The RO decomposition is devel- oped to decompose a corrupted image into the RO components and residual. This is achieved by successively applying RO projections to the image or its residuals to extract the RO components. The RO projections, based on neural networks, extract the closest RO component of an image. The RO reconstruction is aimed to reconstruct the important information, respec- tively from the RO components and residual, as well as to restore the image from this reconstructed information. Experimental results on four tasks, i.e., noise-free image super-resolution (SR), realistic image SR, gray-scale image denoising, and color image denoising, show that the method is effective and efficient for image restoration, and it delivers superior performance for real- istic image SR and color image denoising.
@article{Gao9303377, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Zhuang, Xiahai}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence}, title = {Rank-One Network: An Effective Framework for Image Restoration}, year = {2022}, volume = {44}, number = {6}, pages = {3224-3238}, keywords = {Image restoration;Image reconstruction;Image denoising;Neural networks;Task analysis;Matrix decomposition;Noise reduction;Image restoration;rank one;super resolution;neural network}, doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3046476}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Joint Modeling of Image and Label Statistics for Enhancing Model Generalizability of Medical Image SegmentationShangqi Gao, Hangqi Zhou, Yibo Gao, and 1 more authorIn Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022, Nov 2022
Joint Modeling of Image and Label Statistics for Enhancing Model Generalizability of Medical Image SegmentationShangqi Gao, Hangqi Zhou, Yibo Gao, and 1 more authorIn Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022, Nov 2022Although supervised deep-learning has achieved promising performance in medical image segmentation, many methods cannot generalize well on unseen data, limiting their real-world applicability. To address this problem, we propose a deep learning-based Bayesian framework, which jointly models image and label statistics, utilizing the domain-irrelevant contour of a medical image for segmentation. Specifically, we first decompose an image into components of contour and basis. Then, we model the expected label as a variable only related to the contour. Finally, we develop a variational Bayesian framework to infer the posterior distributions of these variables, including the contour, the basis, and the label. The framework is implemented with neural networks, thus is referred to as deep Bayesian segmentation. Results on the task of cross-sequence cardiac MRI segmentation show that our method set a new state of the art for model generalizability. Particularly, the BayeSeg model trained with LGE MRI generalized well on T2 images and outperformed other models with great margins, i.e., over 0.47 in terms of average Dice. Our code is available at https://zmiclab.github.io/projects.html.
@inproceedings{Gao2022miccai, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Zhou, Hangqi and Gao, Yibo and Zhuang, Xiahai}, editor = {Wang, Linwei and Dou, Qi and Fletcher, P. Thomas and Speidel, Stefanie and Li, Shuo}, title = {Joint Modeling of Image and Label Statistics for Enhancing Model Generalizability of Medical Image Segmentation}, booktitle = {Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention -- MICCAI 2022}, year = {2022}, publisher = {Springer Nature Switzerland}, address = {Cham}, pages = {360--369}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_35}, isbn = {978-3-031-16443-9}, dimensions = {true} }
2021
-
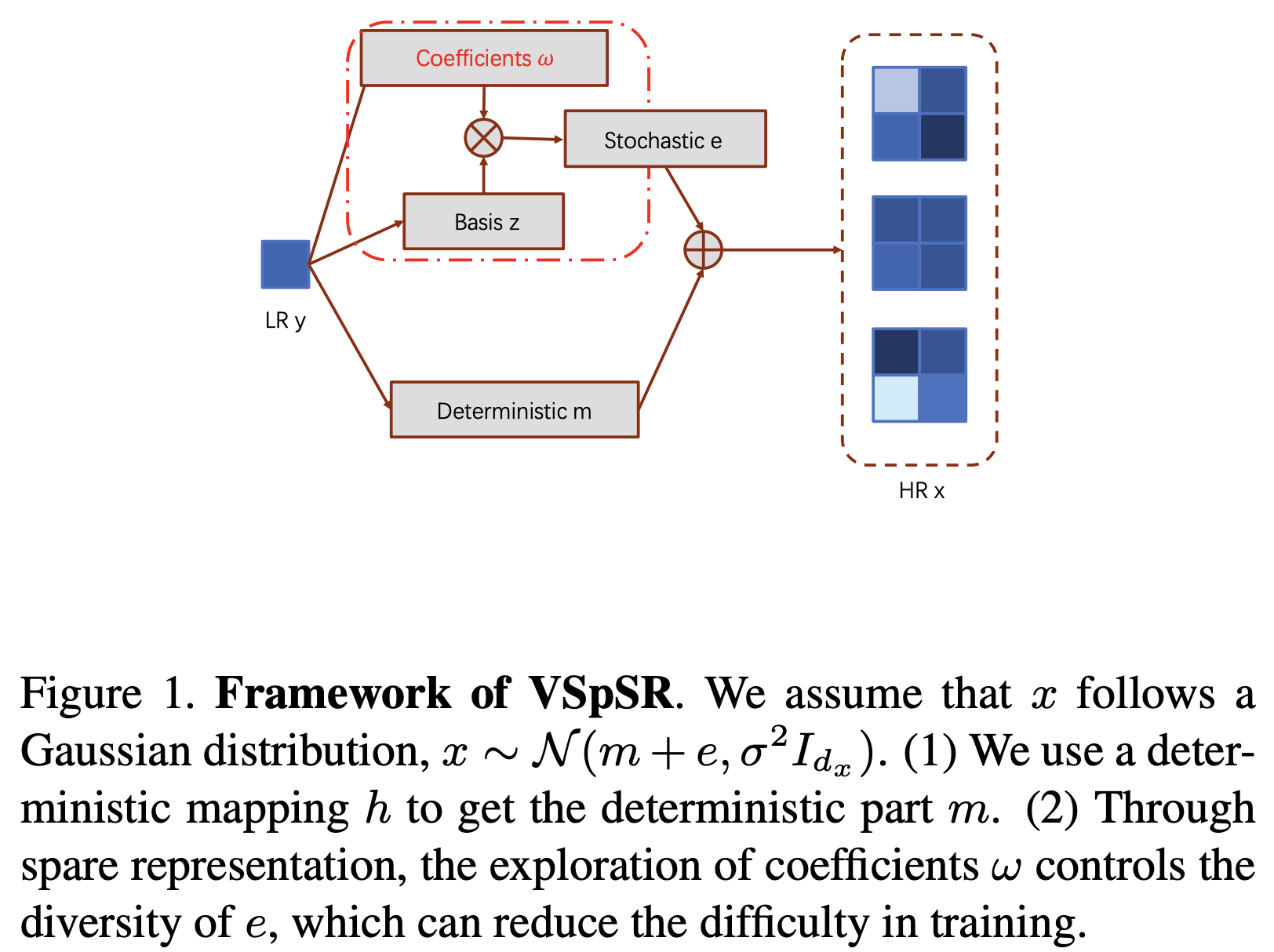 VSpSR: Explorable Super-Resolution via Variational Sparse RepresentationHangqi Zhou, Chao Huang, Shangqi Gao, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Jun 2021
VSpSR: Explorable Super-Resolution via Variational Sparse RepresentationHangqi Zhou, Chao Huang, Shangqi Gao, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Jun 2021@inproceedings{Zhou_2021_CVPR, author = {Zhou, Hangqi and Huang, Chao and Gao, Shangqi and Zhuang, Xiahai}, title = {VSpSR: Explorable Super-Resolution via Variational Sparse Representation}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops}, month = jun, year = {2021}, pages = {373-381}, doi = {10.1109/CVPRW53098.2021.00047}, dimensions = {true} }
2020
-
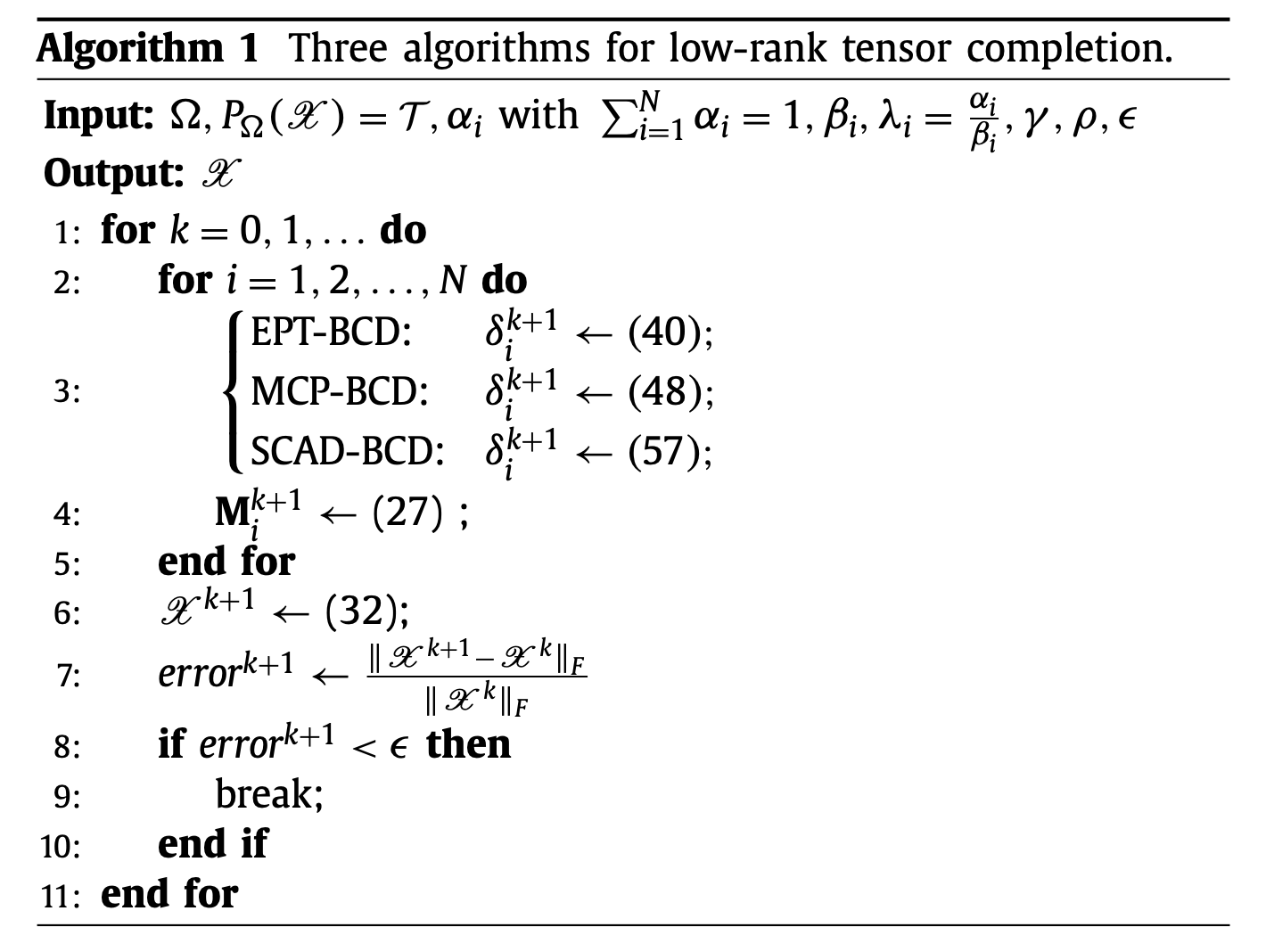 Robust approximations of low-rank minimization for tensor completionShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangNeurocomputing, Jun 2020
Robust approximations of low-rank minimization for tensor completionShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangNeurocomputing, Jun 2020Motivated by the nuclear norm of tensors and nonconvex approximations of matrix rank, we propose three robust approximations of multi-linear rank for tensor completion. For each method, we develop an efficient algorithm to solve the corresponding optimization problem. Besides, we prove that every cluster point of the sequence, generated by the respective algorithm, is a stationary point. To obtain a more robust reconstruction, we design an updating rule of parameters for each method. Our empirical experiments on real-world data show that the proposed methods deliver state-of-the-art performance in the reconstruction of low-rank tensors.
@article{GAO2020319, title = {Robust approximations of low-rank minimization for tensor completion}, journal = {Neurocomputing}, volume = {379}, pages = {319-333}, year = {2020}, issn = {0925-2312}, doi = {10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.086}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231219315280}, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Zhuang, Xiahai}, keywords = {Tensor completion, Block coordinate descent, Nonconvex optimization, Iterative thresholding}, dimensions = {true}, } -
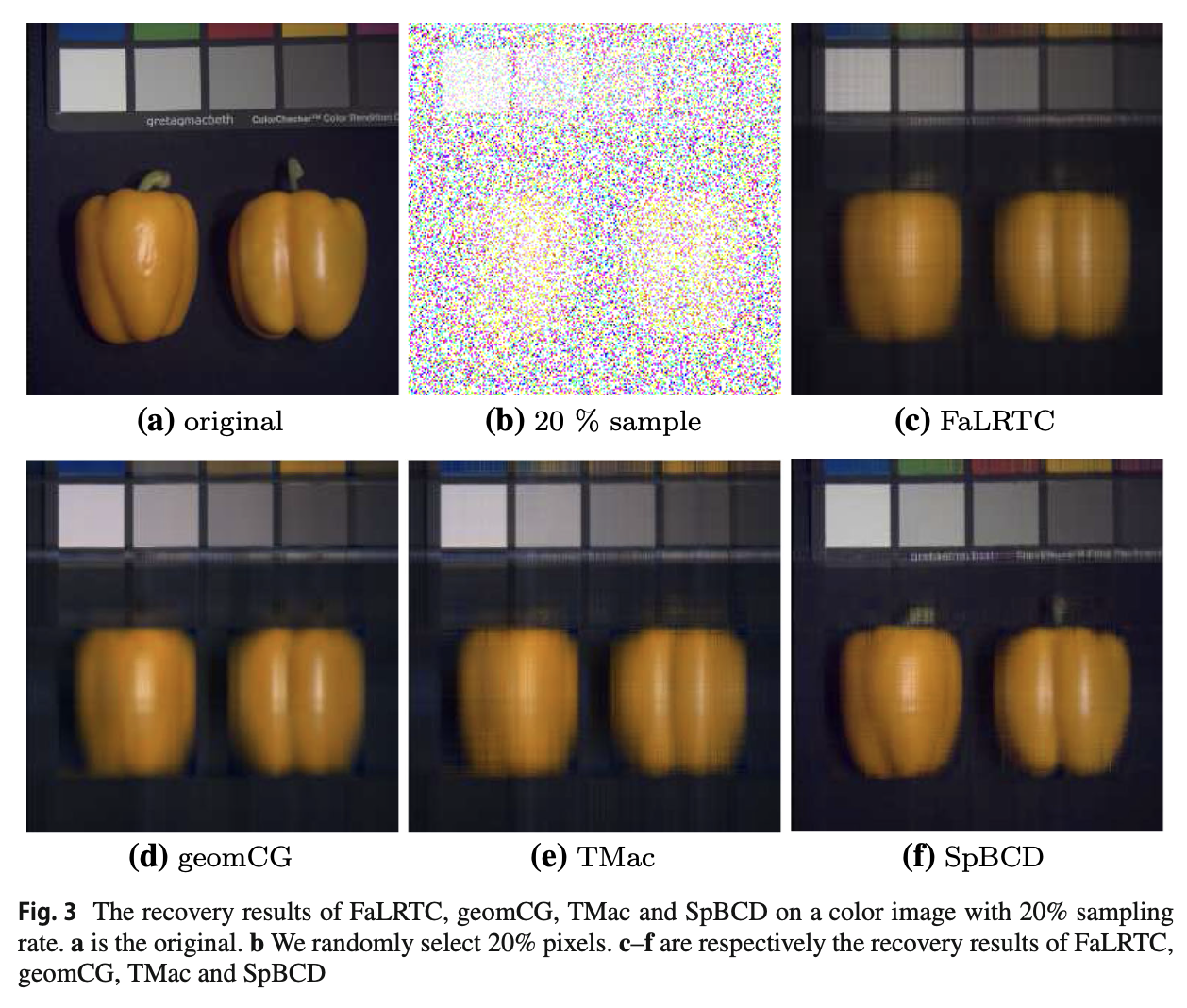 Robust Schatten-p norm based approach for tensor completionShangqi Gao and Qibin FanJournal of Scientific Computing, Jun 2020
Robust Schatten-p norm based approach for tensor completionShangqi Gao and Qibin FanJournal of Scientific Computing, Jun 2020The matrix nuclear norm has been widely applied to approximate the matrix rank for low-rank tensor completion because of its convexity. However, this relaxation may make the solution seriously deviate from the original solution for real-world data recovery. In this paper, using a nonconvex approximation of rank, i.e., the Schatten-p norm, we propose a novel model for tensor completion. It’s hard to solve this model directly because the objective function of the model is nonconvex. To solve the model, we develop a variant of this model via the classical quadric penalty method, and propose an algorithm, i.e., SpBCD, based on the block coordinate descent method. Although the objective function of the variant is nonconvex, we show that the sequence generated by SpBCD is convergent to a critical point. Our numerical experiments on real-world data show that SpBCD delivers state-of-art performance in recovering missing data.
@article{Gao2020robust, title = {Robust Schatten-p norm based approach for tensor completion}, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Fan, Qibin}, journal = {Journal of Scientific Computing}, volume = {82}, pages = {1--23}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Springer}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-01108-9}, doi = {10.1007/s10915-019-01108-9}, dimensions = {true}, }
2019
-
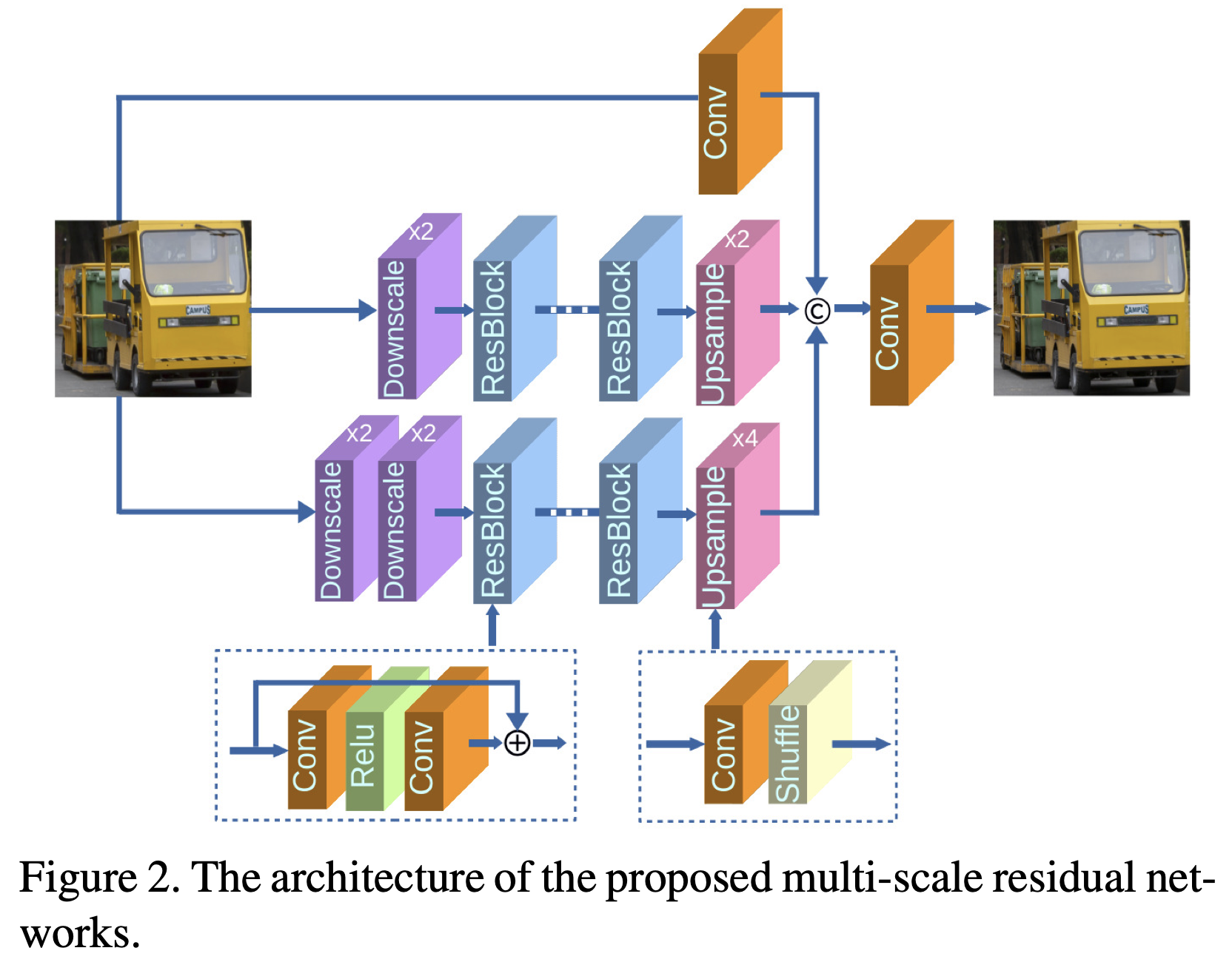 Multi-Scale Deep Neural Networks for Real Image Super-ResolutionShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Jun 2019
Multi-Scale Deep Neural Networks for Real Image Super-ResolutionShangqi Gao and Xiahai ZhuangIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Jun 2019Single image super-resolution (SR) is extremely difficult if the upscaling factors of image pairs are unknown and different from each other, which is common in real image SR. To tackle the difficulty, we develop two multi-scale deep neural networks (MsDNN) in this work. Firstly, due to the high computation complexity in high-resolution spaces, we process an input image mainly in two different downscaling spaces, which could greatly lower the usage of GPU memory. Then, to reconstruct the details of an image, we design a multi-scale residual network (MsRN) in the downscaling spaces based on the residual blocks. Besides, we propose a multi-scale dense network based on the dense blocks to compare with MsRN. Finally, our empirical experiments show the robustness of MsDNN for image SR when the upscaling factor is unknown. According to the preliminary results of NTIRE 2019 image SR challenge, our team (ZXHresearch@fudan) ranks 21-st among all participants. The implementation of MsDNN is released at: https://github.com/shangqigao/gsq-image-SR.
-
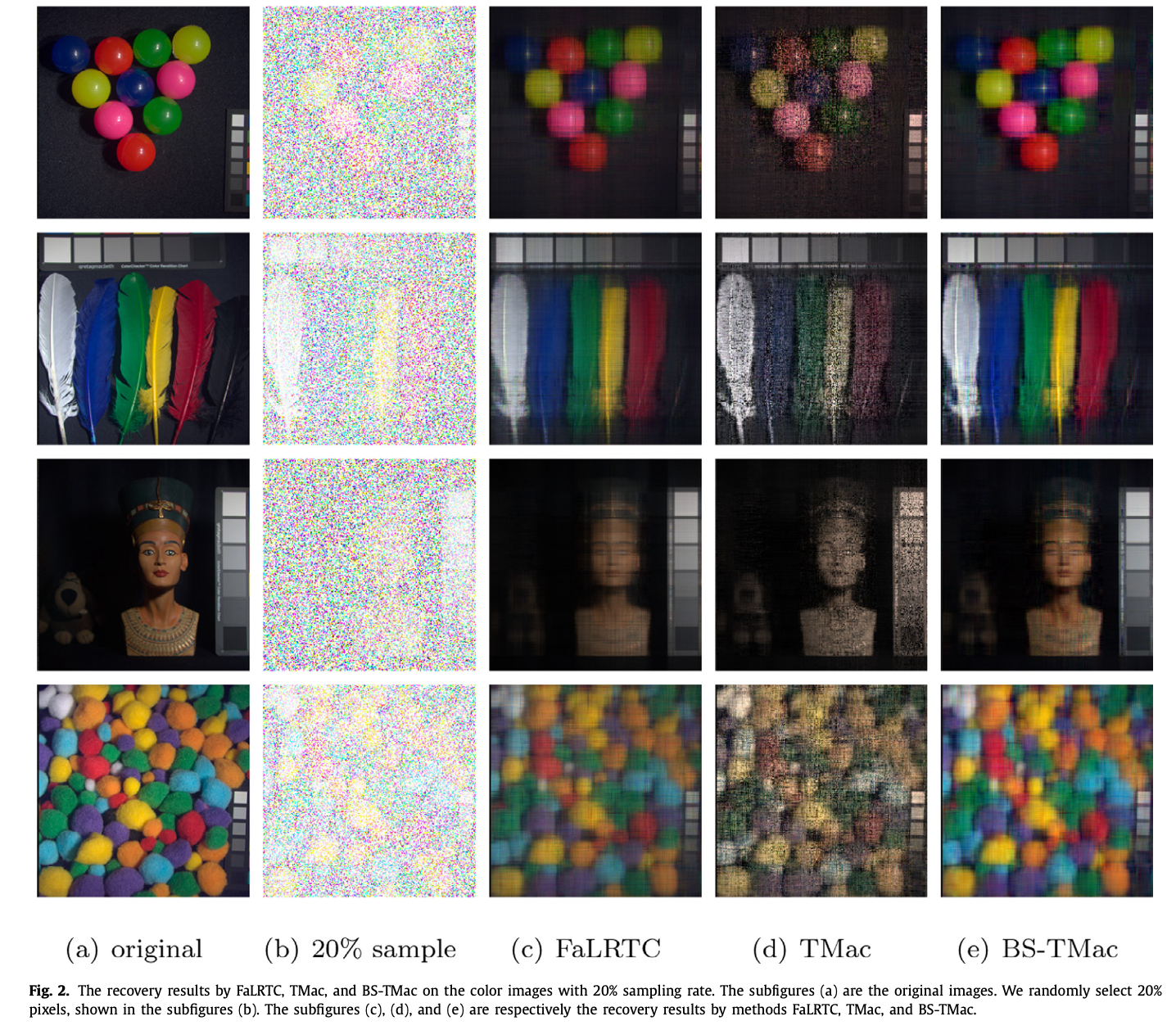 Robust balancing scheme-based approach for tensor completionShangqi Gao and Qibin FanNeurocomputing, Jun 2019
Robust balancing scheme-based approach for tensor completionShangqi Gao and Qibin FanNeurocomputing, Jun 2019Firstly, we propose a balancing scheme called BS to obtain new matricizations for an unbalanced tensor, and develop an efficient algorithm, which employs the idea of Orthogonal-Matching-Pursuit, to implement the BS. Then, we propose a new model for tensor completion based on the BS, and develop an algorithm called BS-TMac, which is rooted from a well known algorithm TMac, to solve the proposed model. Finally, we test our algorithms on synthetic and real world data to show the robustness of the BS-based model in reconstruction for unbalanced tensors. The numerical experiments show that BS-TMac outperforms compared methods in recovery quality.
@article{GAO2019328, title = {Robust balancing scheme-based approach for tensor completion}, journal = {Neurocomputing}, volume = {330}, pages = {328-336}, year = {2019}, issn = {0925-2312}, doi = {10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.033}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231218313614}, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Fan, Qibin}, keywords = {Tensor completion, Balancing scheme, Matching-pursuit}, dimensions = {true}, }
2018
-
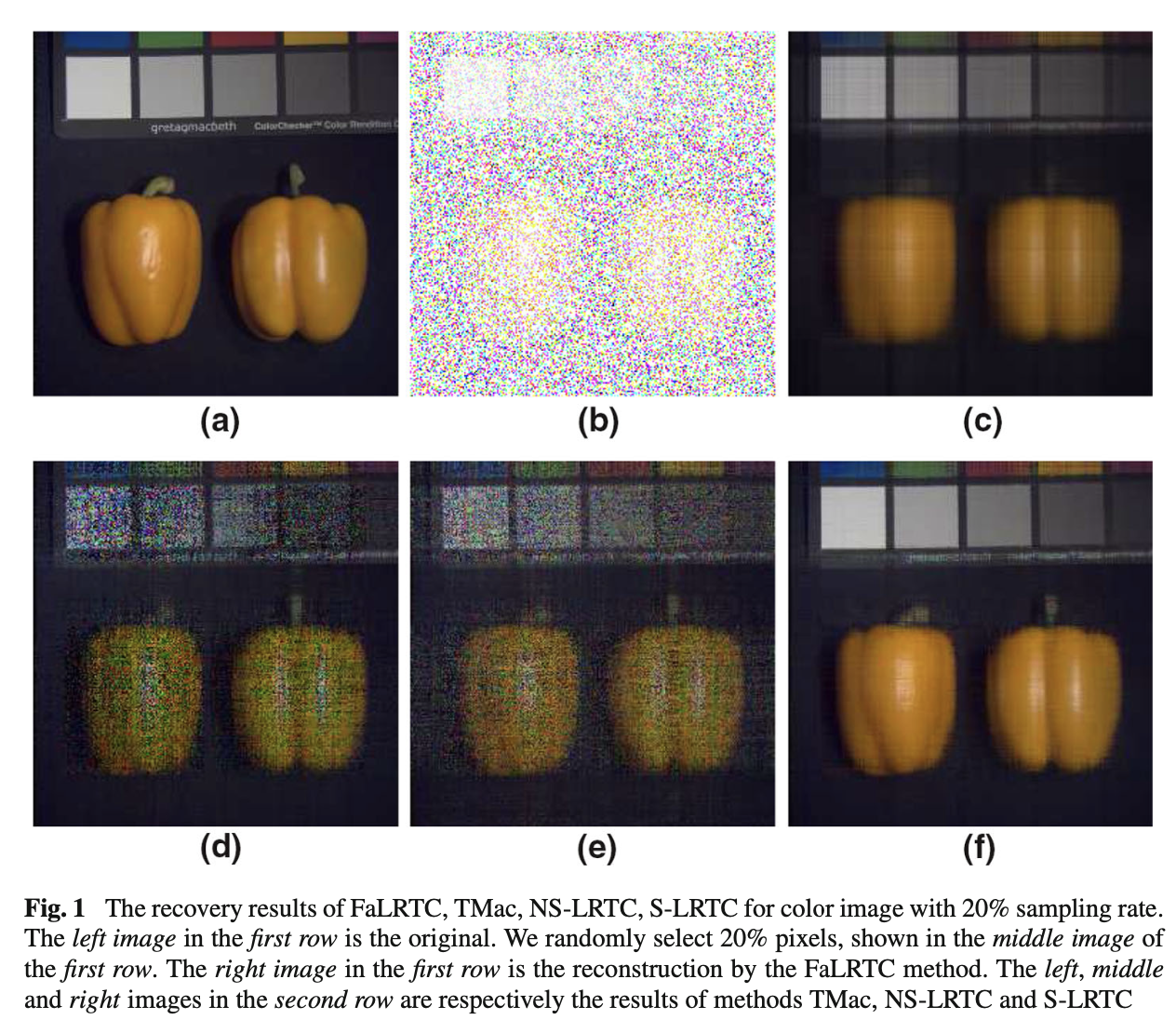 A Mixture of Nuclear Norm and Matrix Factorization for Tensor CompletionShangqi Gao and Qibin FanJ. Sci. Comput., Jun 2018
A Mixture of Nuclear Norm and Matrix Factorization for Tensor CompletionShangqi Gao and Qibin FanJ. Sci. Comput., Jun 2018In this paper, we propose a mixture model for tensor completion by combining the nuclear norm with the low-rank matrix factorization. To solve this model, we develop two algorithms: non-smooth low-rank tensor completion (NS-LRTC), smooth low-rank tensor completion (S-LRTC). When the sampling rate (SR) is high, our experiments on real-world data show that the NS-LRTC algorithm outperforms other tested methods in running time and recovery quality. In addition, whatever the SR is, the proposed S-LRTC algorithm delivers state-of-art recovery performance compared with other tested approaches. Although the objective function in our model is non-convex and non-differentiable, we prove that every cluster point of the sequence generated by NS-LRTC or S-LRTC is a stationary point.
@article{Gao2018JSC, author = {Gao, Shangqi and Fan, Qibin}, title = {A Mixture of Nuclear Norm and Matrix Factorization for Tensor Completion}, year = {2018}, issue_date = {April 2018}, publisher = {Plenum Press}, address = {USA}, volume = {75}, number = {1}, issn = {0885-7474}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-017-0521-9}, doi = {10.1007/s10915-017-0521-9}, journal = {J. Sci. Comput.}, pages = {43–64}, numpages = {22}, keywords = {Tensor completion, Nuclear norm, Matrix factorization, Block coordinate descent}, dimensions = {true}, }






